Medications Guide – Alternatives, Safety, and What’s New in 2025
If you’ve ever wondered whether there’s a better pill for a condition, you’re not alone. Many people switch meds because of side effects, cost, or just because a newer option promises better results. This page pulls together the most asked‑about alternatives, safety pointers, and quick facts about the drugs that are shaping 2025.
Why Look for Medication Alternatives?
First off, not every drug works the same for everyone. Your genetics, other meds, and lifestyle can change how a pill feels. For example, some athletes with joint pain are trying diacerein as a non‑steroidal option that targets inflammation differently. Others with hypothyroidism are exploring alternatives to Levothyroxine because they experience mood swings or weight changes on the standard dose. When a medication clashes with your daily routine or triggers unwanted symptoms, a safe alternative can be a game changer.
Cost is another driver. Brand‑name antibiotics like Zithromax or Vibramycin can be pricey, especially without insurance. Knowing cheaper, equally effective substitutes helps you stay on track without breaking the bank. Finally, newer science brings fresh players to the field. The weight‑loss world, for instance, is buzzing about Semaglutide alternatives such as Retatrutide, which aim to give similar results with different dosing schedules.
Top Alternatives to Watch in 2025
Diacerein for athletes: This IL‑1 inhibitor reduces cartilage breakdown and may ease stubborn joint pain without the stomach upset common to NSAIDs. Typical dosing starts at 50 mg twice daily, but a doctor will adjust based on how you feel. Keep an eye on liver tests if you stay on it for more than a few months.
Semaglutide alternatives: If injections aren’t your thing, look at next‑gen GLP‑1 agonists like Retatrutide or oral options entering the market. They often have similar appetite‑suppressing effects but differ in dosing frequency – some are once‑weekly, others twice‑daily. Side effects still include nausea, so start low and build up.
Levothyroxine substitutes: Options such as Liothyronine (T3) or combination T4/T3 pills can smooth out energy crashes that some people feel on pure T4 therapy. Blood‑test monitoring is key because the body handles T3 faster, which can swing thyroid levels quickly.
Antibiotic swaps: For those who can’t take Zithromax, drugs like Levofloxacin, Azithromycin, or newer macrolides offer once‑daily dosing and good coverage for respiratory infections. If you need a broader spectrum, consider a fluoroquinolone, but watch for tendon‑related warnings.
Vibramycin alternatives: Tetracycline‑class drugs such as Minocin or Sumycin work well for certain skin and lung infections. They’re taken twice a day and have fewer photosensitivity issues than the older tetracycline, but they still aren’t ideal for pregnant women.
When you’re weighing any of these options, talk to your pharmacist or doctor about drug interactions, what labs you’ll need, and how long you should stay on the new medication. Most alternatives work best when you give them a few weeks to settle in.
Bottom line: you don’t have to stay stuck on one pill forever. By staying informed about the latest alternatives and checking in regularly with your healthcare team, you can pick a medication that fits your life, budget, and health goals. Keep this page bookmarked – the list will grow as new studies and drugs hit the market.

28
Feb
Generic Drug Safety: Are Generics as Safe as Brand Names?
Generic drugs are just as safe and effective as brand-name medications for most people. The FDA requires strict bioequivalence testing, and large studies confirm they work the same. Exceptions exist for narrow therapeutic index drugs like levothyroxine or warfarin, where monitoring is advised.

21
Feb
Why Generic Combination Products Improve Patient Compliance
Generic combination products simplify treatment by merging drugs and devices into one unit, improving adherence and cutting costs. Learn how they help patients stick to their regimens - and why education is key.
7
Feb
Narrow Therapeutic Index Drugs: What Patients Need to Know
Narrow therapeutic index drugs require extreme precision in dosing. Learn what they are, which common medications fall into this category, why generic switches can be risky, and how to stay safe with regular monitoring and consistent sources.

5
Feb
Insurer Pressure on Generic Drug Substitution: Provider Strategies and Challenges
Insurers push for generic drugs to cut costs, but providers face administrative hurdles and patient risks. Learn how doctors navigate prior auth, step therapy, and state laws to balance care and compliance.
2
Feb
High-Protein Diets and Levodopa: How Food Affects Parkinson's Motor Control
High-protein meals can block levodopa from reaching the brain in Parkinson’s patients, causing unpredictable motor fluctuations. Learn how to adjust your diet to improve medication effectiveness and regain mobility.

1
Feb
Evergreening: How Pharmaceutical Brands Stretch Patents to Block Generic Drugs
Evergreening lets drug companies extend patents on old medications through minor tweaks, blocking cheaper generics and keeping prices high. Learn how it works, who does it, and what it means for patients.

31
Jan
Cough and Cold Medicine Safety for All Ages: What Actually Works and What to Avoid
Many OTC cough and cold medicines don't work and can be risky, especially for kids. Learn which ingredients to avoid, what actually helps, and safer alternatives backed by science.

28
Jan
Infographics About Generics: Visual Tools to Understand Generic Medications
Infographics about generics help patients understand that generic drugs are just as safe and effective as brand-name versions. Learn how visual tools from the FDA and other experts are improving medication adherence and cutting healthcare costs.

26
Jan
Pediatric Safety: What Parents and Doctors Need to Know About Generic Drugs for Children
Generic drugs for children aren't always safe just because they're cheaper. Learn the hidden risks, key drugs to avoid, and practical steps every parent and caregiver should take to prevent dangerous medication errors.
26
Jan
Authorized Generics vs Brand Drugs: What You Need to Know About Identical Medications
Authorized generics are identical to brand-name drugs in every way-active ingredients, fillers, and manufacturing. They’re often cheaper and safer for sensitive patients. Here’s how to get them and why they’re not the same as regular generics.
24
Jan
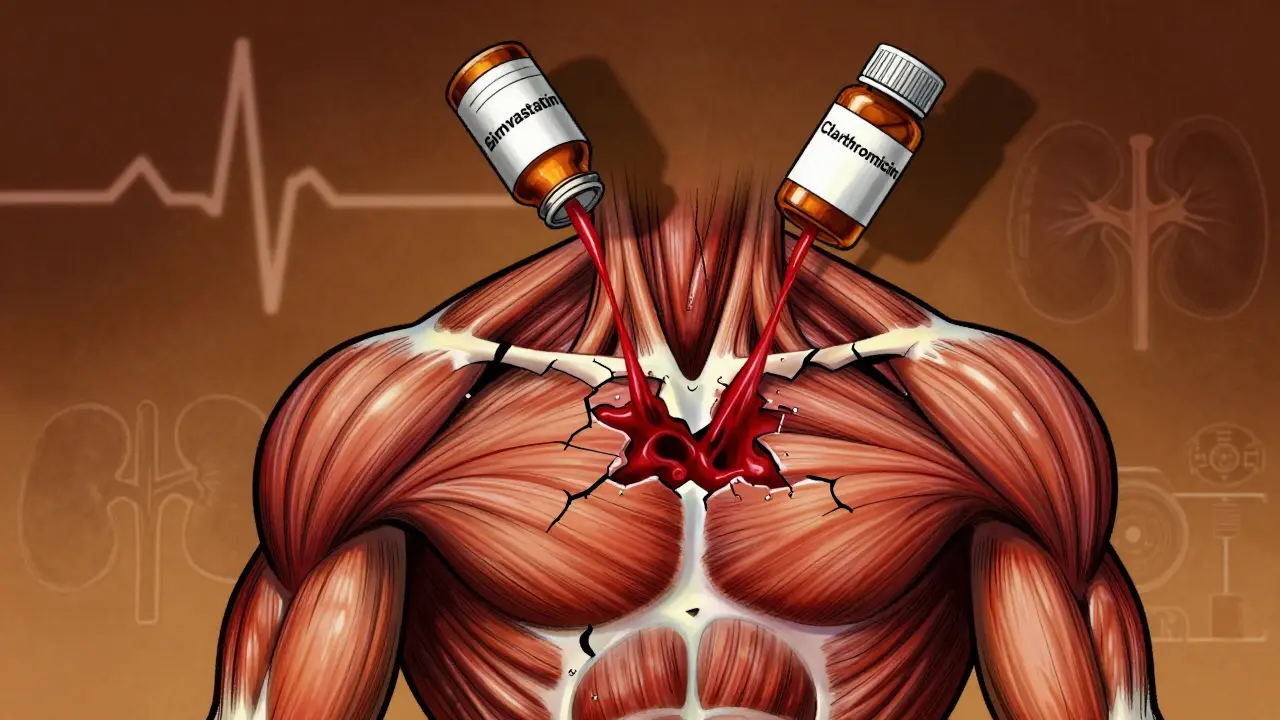
Rhabdomyolysis from Medication Interactions: How Common Drug Combos Cause Muscle Breakdown
Medication interactions can trigger rhabdomyolysis - a dangerous muscle breakdown that harms kidneys and can be fatal. Learn which drug combos are most risky, who’s most vulnerable, and how to prevent it.

23
Jan
What Are Biosimilars? A Simple Guide for Patients
Biosimilars are highly tested, FDA-approved versions of complex biologic drugs. They work the same as the original but cost less. Learn how they differ from generics and why they’re safe for patients.